Reputation plugin
This plugin is designed to monitor the reputation of various objects and adjust scores accordingly.
For instance, if you have a DKIM domain that is known to be used for spam, this module enables you to decrease the negative score of the DKIM_ALLOW symbol, or even add some score.
Conversely, if a domain has a high reputation, the DKIM_ALLOW score will have a more negative score (like auto-whitelisting) and increase the score for DKIM_REJECT accordingly (since the message looks like a phishing attempt).
Additionally, this module encompasses the functionality of the following modules:
- ip_score - by means of
ipcomponent - url_reputation - by means of
urlcomponent (removed in Rspamd 2.0)
Configuration and principles of work
Like many other modules, this module requires a set of rules to be defined. Each rule comprises the following components:
- Selector configuration - specifies the data to be extracted from a message and defines data processing logic
- Backend configuration - determines where reputational tokens should be stored and queried. For instance, Redis can be used for both storing and extracting, while DNS can only be used as a read-only storage
- Common configuration - defines generic rule parameters, such as a symbol, that are not related to either the backend or the selector
Below are a few examples of such configurations:
# local.d/reputation.conf
rules {
ip_reputation = {
selector "ip" {
}
backend "redis" {
servers = "localhost";
}
symbol = "IP_REPUTATION";
}
spf_reputation = {
selector "spf" {
}
backend "redis" {
servers = "localhost";
}
symbol = "SPF_REPUTATION";
}
dkim_reputation = {
selector "dkim" {
}
backend "redis" {
servers = "localhost";
}
symbol = "DKIM_REPUTATION"; # Also adjusts scores for DKIM_ALLOW, DKIM_REJECT
}
generic_reputation = {
selector "generic" {
selector = "ip"; # see https://docs.rspamd.com/configuration/selectors
}
backend "redis" {
servers = "localhost";
}
symbol = "GENERIC_REPUTATION";
}
}
You also need to define the scores for symbols added by this module:
# local.d/groups.conf
group "reputation" {
symbols = {
"IP_REPUTATION_HAM" {
weight = -1.0;
}
"IP_REPUTATION_SPAM" {
weight = 4.0;
}
"DKIM_REPUTATION" {
weight = 1.0;
}
"SPF_REPUTATION_HAM" {
weight = -1.0;
}
"SPF_REPUTATION_SPAM" {
weight = 2.0;
}
"GENERIC_REPUTATION" {
weight = 1.0;
}
}
}
The weight assigned to these symbols are merely examples and you should adjust them to fit your particular situation.
The image below illustrates the process of reputation token handling:
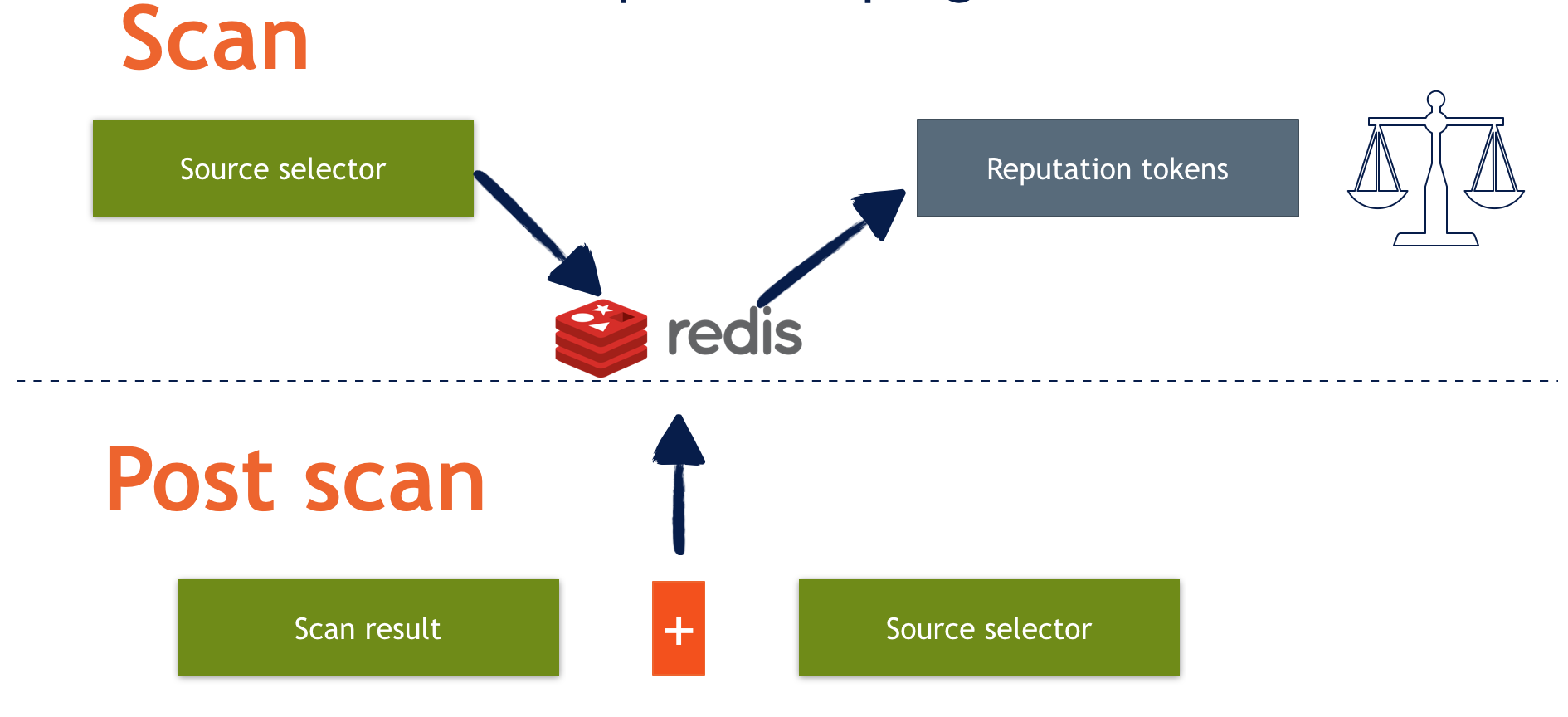
Backends configuration and principles of work
Selectors provide what are known as tokens for backends. For instance, in the case of IP reputation, these tokens could be asn, ipnet, and country. Each token is mapped to a particular key in the backend. In the case of Redis backend, there is a concept of buckets, with each bucket containing a set of counters that indicate the number of messages with a specific action:
- number of spam messages
- number of ham messages
- number of probable spam (junk) messages
When filling these buckets, the score may also be taken into account. Additionally, each bucket has two other attributes:
- time window;
- score multiplier;
Each bucket uses discrete time windows that are specified. By default, one bucket with a time window of 30 days is defined for Redis:
buckets = [
{
time = 60 * 60 * 24 * 30,
name = '1m',
mult = 1.0,
}
];
Upon bucket lookup, you have the following attributes:
- Number of messages of the each class (let's say
h,s,j) - Bucket score (e.g.
1.5for short term bucket) - Combination formula defined in the selector:
$$ f(buckets)=\sum_{i=1}^n {(spam_{i} * mult_{spam} + ham_{i} * mult_{ham} + junk_{i} * mult_{junk}) * bscore_{i}} $$
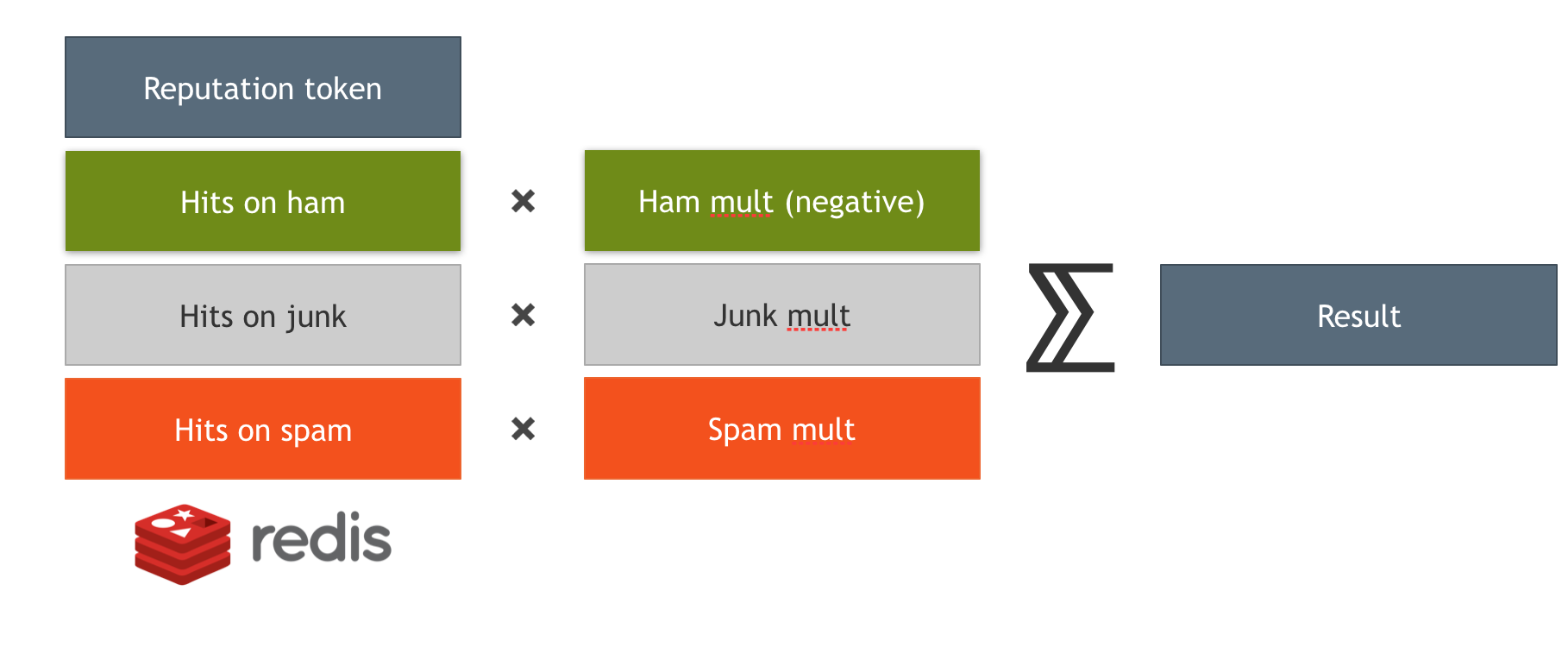
Selector types
There are couple of pre-defined selector types, specifically:
- SPF reputation -
spfselector - DKIM reputation -
dkimselector - IP, asn, country and network reputation -
ipselector - URLs reputation -
urlselector - Generic reputation based on selectors framework -
genericselector
All selector types except for generic do not require explicit configuration. The generic selector, on the other hand, necessitates the setting of a selector attribute. For more advanced selector configurations, you may refer to the module's source code.
Common selector options
All selectors support the following common options:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
lower_bound | 10 | Minimum number of messages before reputation scoring kicks in |
min_score | nil | Minimum reputation score |
max_score | nil | Maximum reputation score |
outbound | true | Apply reputation to outbound messages |
inbound | true | Apply reputation to inbound messages |
split_symbols | false | Create separate _HAM and _SPAM symbols instead of a single symbol |
exclusion_map | nil | Map of items to exclude from reputation tracking |
IP selector specific options
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
ipv4_mask | 32 | Mask bits for IPv4 addresses |
ipv6_mask | 64 | Mask bits for IPv6 addresses |
asn_prefix | a: | Prefix for ASN hashes |
country_prefix | c: | Prefix for country hashes |
ip_prefix | i: | Prefix for IP hashes |
DKIM selector specific options
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
max_accept_adjustment | 2.0 | Maximum score adjustment for accepted DKIM signatures |
URL selector specific options
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
max_urls | 10 | Maximum number of URLs to check per message |
check_from | true | Check URLs from the From domain |
Generic selector specific options
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
selector | required | Selector expression (see selectors documentation) |
delimiter | : | Delimiter for multiple selector results |
whitelist | nil | Map of whitelisted selector values |