Greylisting module
The purpose of this module is to delay messages that have a spam score above the greylisting action threshold.
Principles of work
When the Greylisting module is enabled, two hashes are saved for each message in Redis:
- meta hash is based on SMTP envelope
from, all sorted SMTPrecipients, and masked senderIP - data hash is based on the message body (up to
max_data_len),subject, all sorted SMTPrecipients, and MIMEFromaddress
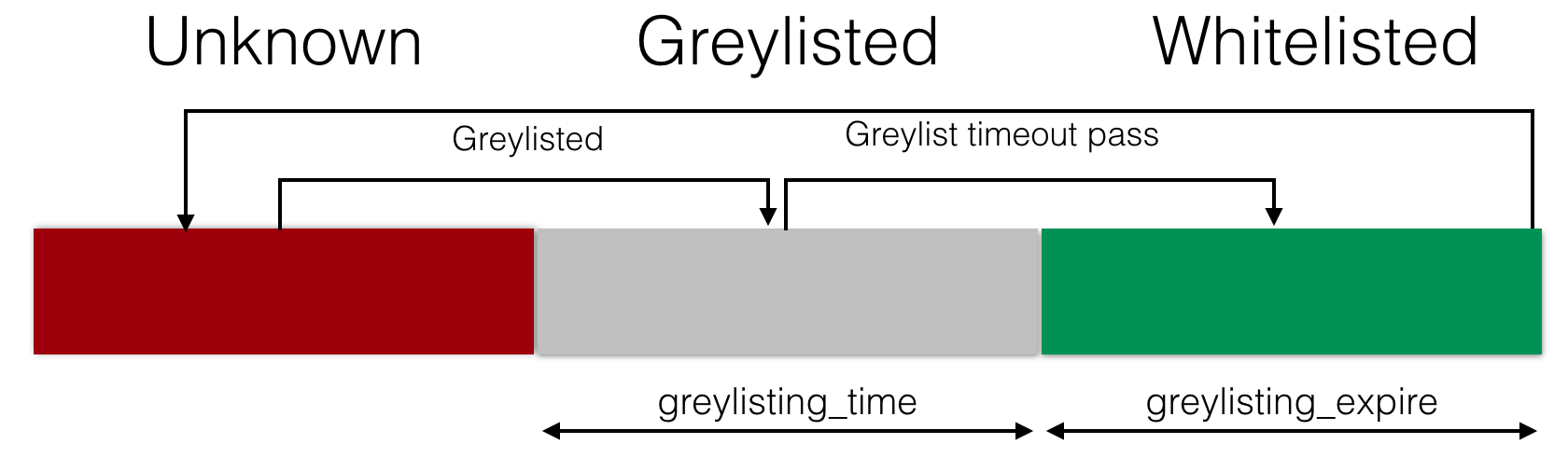
IP address is stored with certain mask applied: it is /19 for IPv4 and /64 for IPv6 accordingly. Each hash has its own timestamp and Rspamd checks for the following times:
greylistingtime - when a message should be temporary rejectedexpiretime - when a greylisting hash is stored in Redis
The hashes lifetime is depicted in the following scheme:
The greylisting module triggers a soft reject action, which is intended to be interpreted by the MTA as a temporary rejection (typically through the Milter interface). For Exim, you can configure it to recognize soft reject using the guidelines provided in the integration guide for details. For Haraka, support is available from version 2.9.0 onward.
Module configuration
To use the greylisting module, you must first set up a Redis server to store hashes. You can find detailed instructions on how to do this in the following document. Once the Redis server is set up, you can modify a few specific options for the greylisting module. It is recommended that you define these options in local.d/greylist.conf:
expire: setup hashes expire time (1 day by default)timeout: defines greylisting timeout (5 min by default)greylist_min_score: messages with scores below this threshold are not greylisted; if unset, falls back to thegreylistaction threshold from metricsipv4_mask: mask to apply for IPv4 addresses (19 by default)ipv6_mask: mask to apply for IPv6 addresses (64 by default)key_prefix: prefix for hashes to store in Redis (rgby default)max_data_len: maximum length of data to be used for body hash (10kB by default)message: a message for temporary rejection reason (Try again laterby default)message_func: Lua function to generate custom rejection message; receivestaskandend_timeas argumentssymbol: symbol name to insert on greylisting (GREYLISTby default)action: action to apply when greylisting (soft rejectby default; usegreylistfor Exim)whitelisted_ip: map of IP addresses and/or subnets to skip greylisting forwhitelist_domains_url: map of hostnames and/or eSLDs of hostnames to skip greylisting forwhitelist_symbols: skip greylisting when specific symbols have been found (from 1.9.1)report_time: tell when greylisting is expired (appended tomessage);falseby defaultcheck_local: greylist messages from local networks (falseby default)check_authed: greylist messages from authenticated users (falseby default)
If you want to skip greylisting based on other conditions, you can simply disable the GREYLIST_CHECK and GREYLIST_SAVE symbols using the settings module.
To enable the module with its default settings, you must define at least one redis server to store greylisting data. You can do this by adding the following lines to local.d/greylist.conf:
# local.d/greylist.conf
servers = "127.0.0.1:6379";
Adding servers to store greylisting data enables greylisting in Rspamd.